In the AL language for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, the Dictionary data type represents an unordered collection of keys and values optimized for fast lookup of values. In a Dictionary, each key is unique and is used to access its corresponding value. The dictionary data type allows you to store key-value pairs where there …
Tag: AL
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2024/07/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-decoding-dictionaries-unlocking-the-power-of-key-value-pairs/
Jul 08 2024
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central: Navigating Lists
In the AL language for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, a List data type is a strongly typed list of ordered objects accessed by index, starting at 1. Lists are a great alternative to arrays. Unlike arrays, lists are unbounded, which means their size doesn’t need to be declared upon creation and can grow dynamically …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2024/07/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-navigating-lists/
Feb 07 2024
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central: My Adventures with the BaseApp Contribution Pilot
In October 2022, Microsoft announced a new open-source program for the Business Central Base Application, the solution’s core functionality. The program allows partners and community members to contribute code and suggestions to the Base Application. The open-source program for Business Central is an excellent opportunity for anyone who wants to learn more about the solution, …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2024/02/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-my-adventures-with-the-baseapp-contribution-pilot/
Jul 24 2023
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central – Sorting Algorithms: Bubble, Merge, and Quick
The other day I felt my computer files were a little disorganized, so I went through some old files to do some hard-core cleanup. I wanted to purge and archive old programs, documents, and repos. While reviewing the files, I found some old C# code (from the days of when I tried to stay sharp …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/07/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-sorting-algorithms-bubble-merge-and-quick/
Jun 04 2023
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central – Split Delimited Value in AL
In the AL language for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, the List Data Type represents a strongly typed list of ordered objects accessible by index. Lists are unbounded, meaning their dimension (size) is not specified when declared. A List can only be declared with simple types (Byte, Boolean, Char, Code, Date, DateFormula, DateTime, Decimal, Text, …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/06/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-split-delimited-value-in-al/
May 22 2023
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central – Base64 Encoding and Decoding
Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes representing binary data in an ASCII string format. Base64 data encoding is designed to survive transport through transport layers that are not 8-bit clean, such as mail bodies. Encoding the binary data to ASCII text helps ensure that the data remains intact without loss or modification during …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/05/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-base64-encoding-and-decoding/
Apr 25 2023
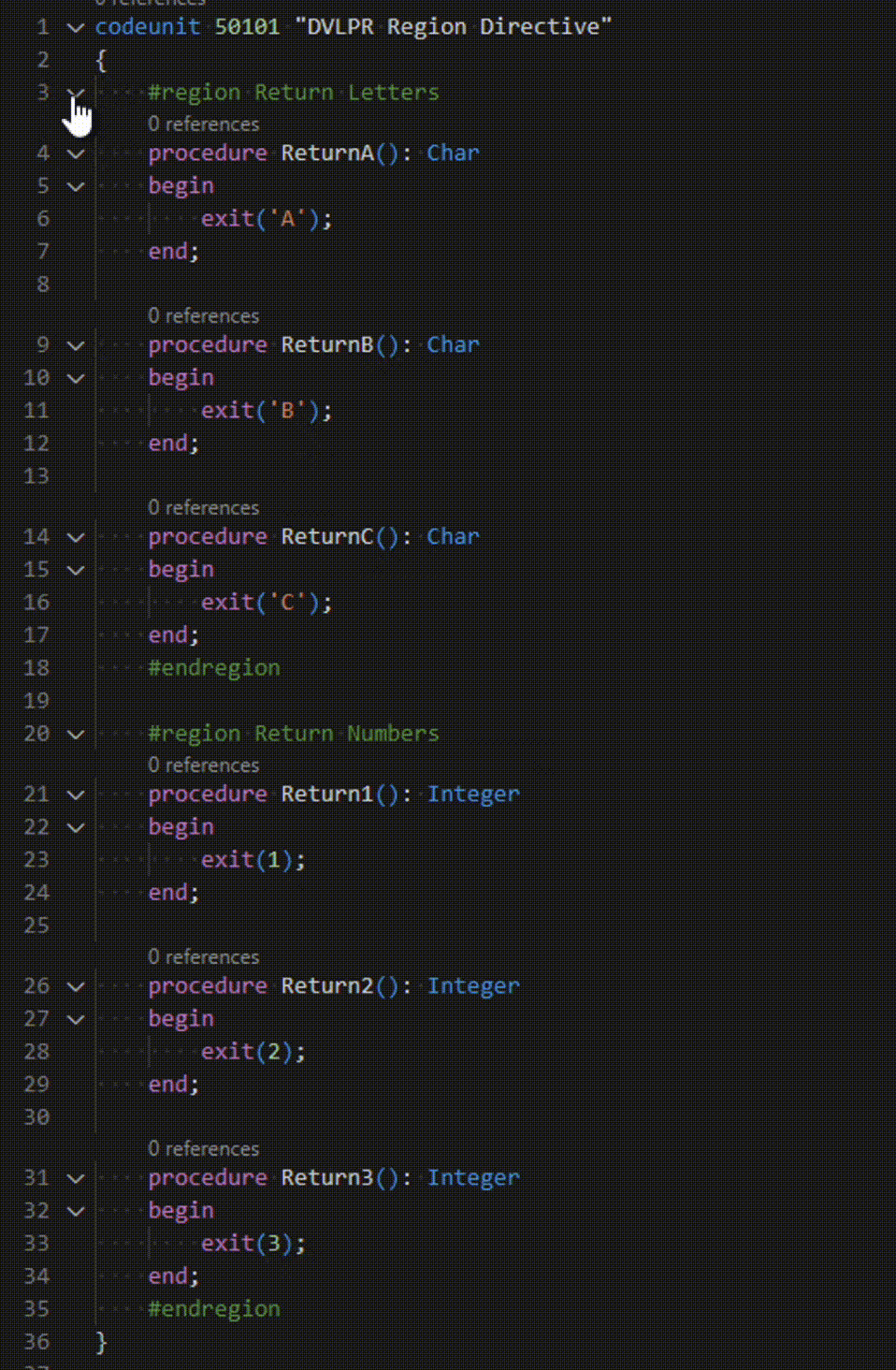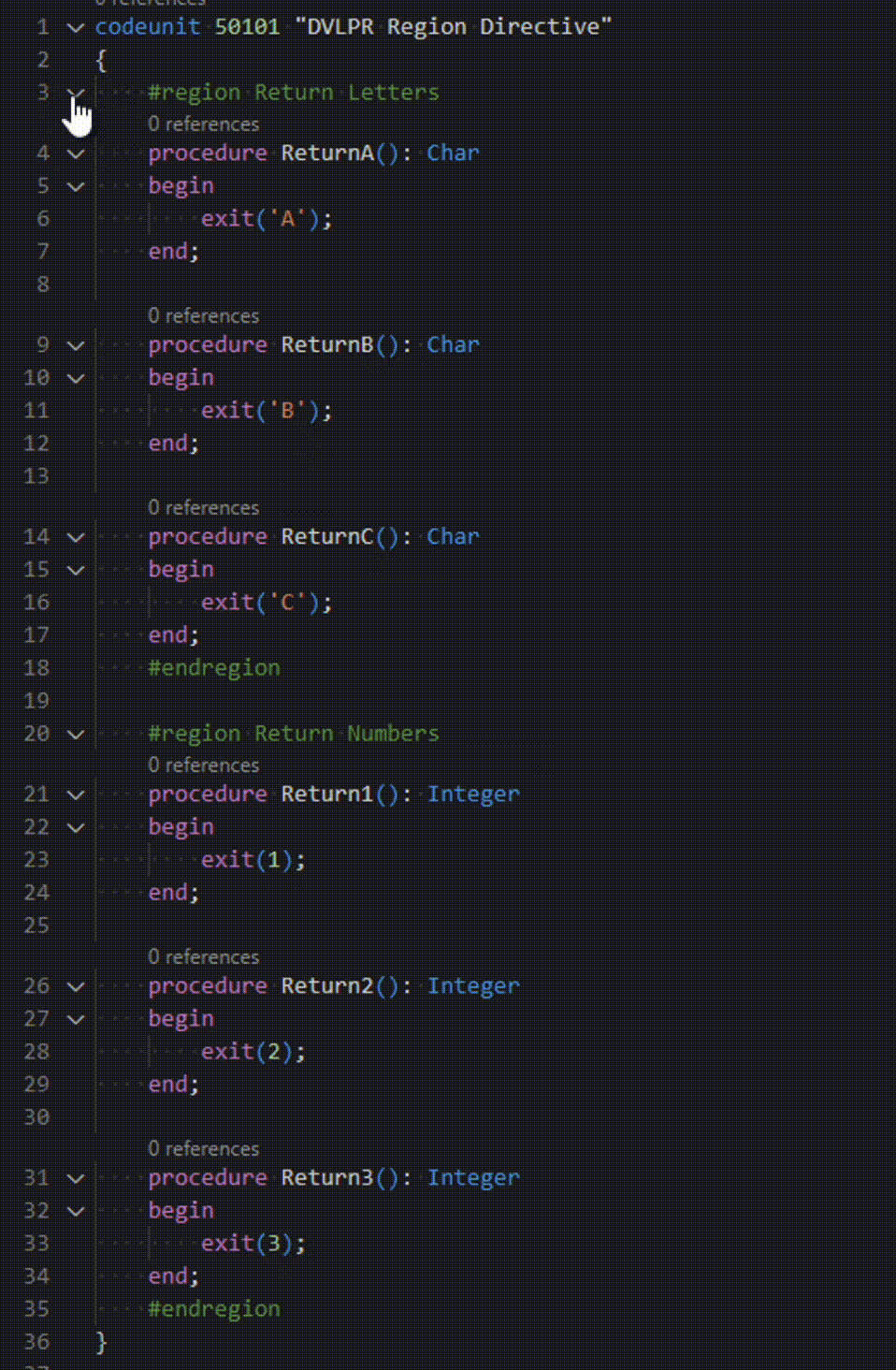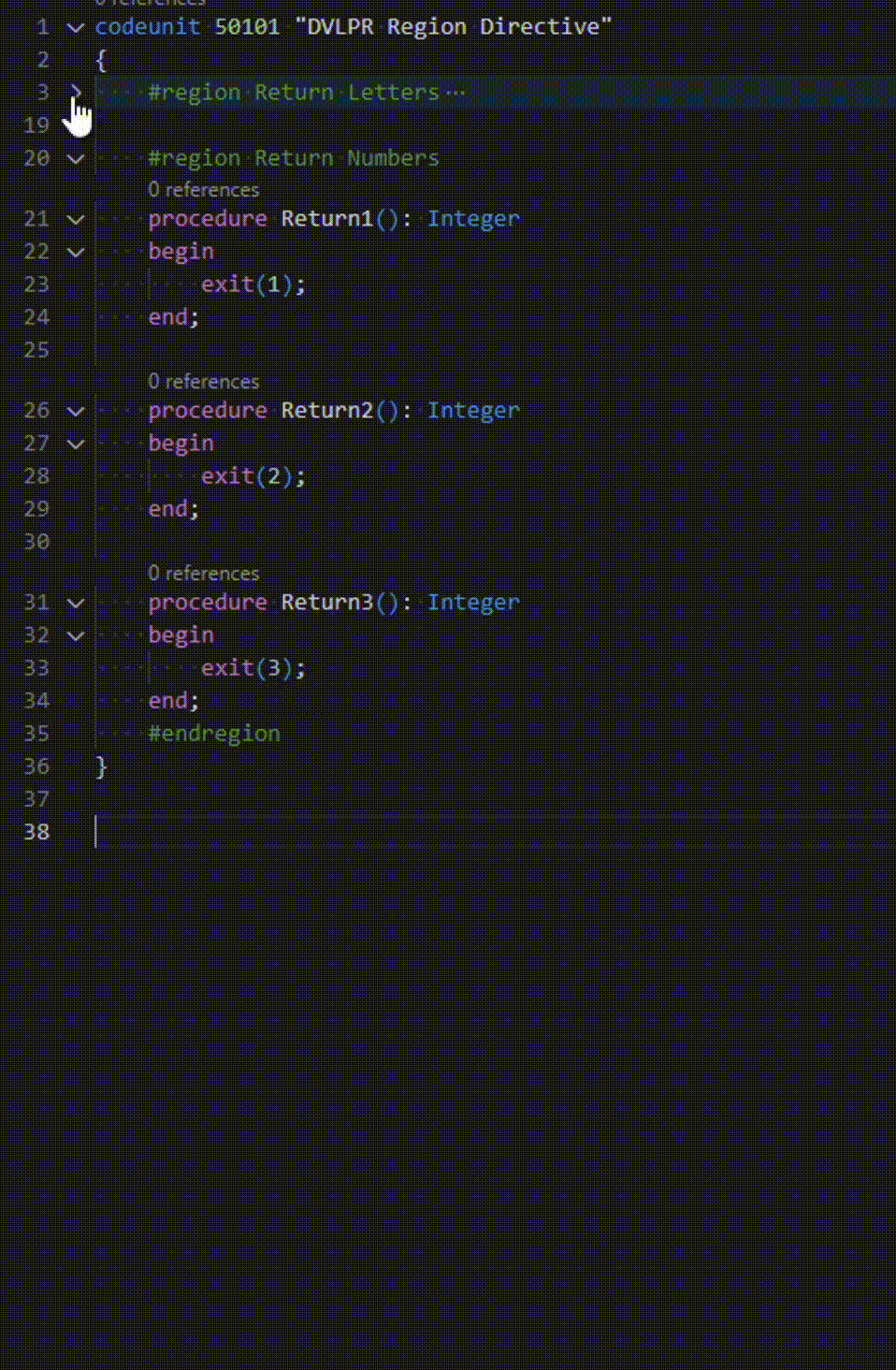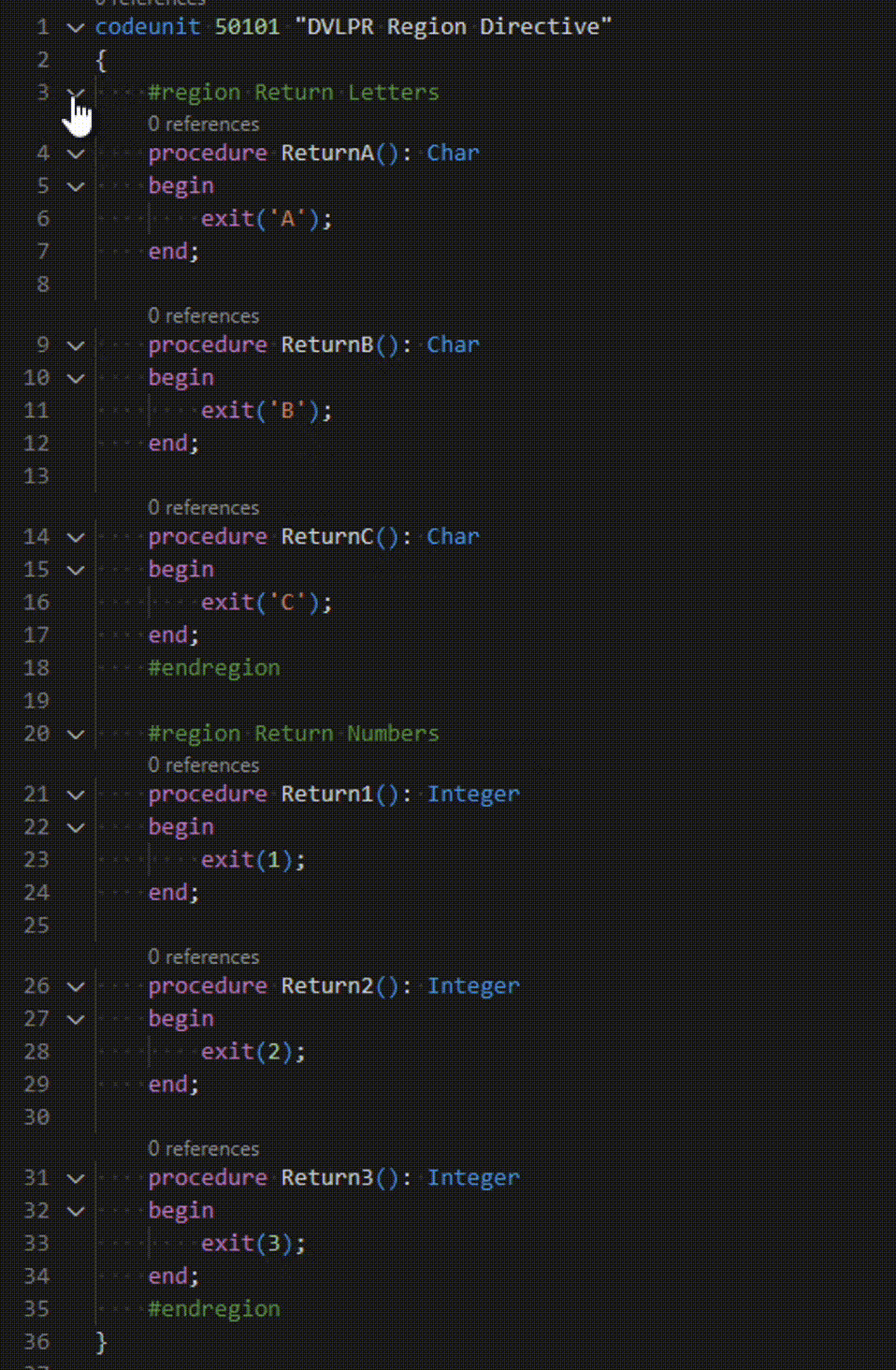
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central – AL Region Directive
In the AL programming language, region directives are used to organize code to a specific region or section of code. Regions can help developers keep track of and manage the code for different parts of an application. The Region Directives also mark a block of code that you can expand or collapse, which is helpful …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/04/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-al-region-directive/
Apr 21 2023
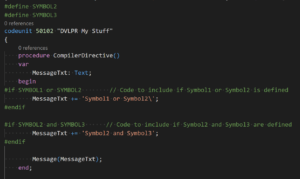
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central – AL Conditional Preprocessor Directives
In the AL programming language, preprocessor directives are used to make code conditional, suppress warnings, and enable code expansion and collapse. The AL preprocessor directives are grouped into conditional, regions, and pragmas categories. In this article, I’ll highlight Conditional Preprocessor Directives. Conditional preprocessor directives are a feature in AL that allows developers to include or …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/04/microsoft-dynamics-365-business-central-al-conditional-preprocessor-directives/
Jan 05 2023
Dynamics 365 Business Central – TryFunction
The TryFunction attribute in AL, when developing for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, indicates that a method is a Try method. A Try method in AL enables you to handle errors that occur in the application during code execution. For example, with try methods, you can provide more user-friendly error messages or manage the execution …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2023/01/dynamics-365-business-central-tryfunction/
Dec 29 2022
Dynamics 365 Business Central – JSON Object into a Dictionary Data Type
The Dictionary Data Type represents an unordered collection of keys and values and is optimized for fast lookup of values. Each addition to the dictionary consists of a value and its associated key. Every key in a Dictionary must be unique. It is on my list of favorite “new” AL Data Types, and I find …
Permanent link to this article: https://www.dvlprlife.com/2022/12/dynamics-365-business-central-json-object-into-a-dictionary-data-type/